Smarter SQL Server Automation with Ansible Handlers: Restart Only When Needed
Oct 10, 2025
How many times have you applied a configuration change and SQL Server restarted, even though nothing actually changed?
- Scripts run blindly
- Unnecessary downtime interrupts users
- You lose trust from the business because "maintenance" caused avoidable outages.
Fragile scripts don't know the difference between changed and unchanged. Ansible does — with handlers.
What Are Handlers?
Handlers are tasks that only run when notified.
- If a task makes a change, Ansible notifies the handler.
- If no change occurs, the handler does nothing.
- Executed at the end of a play. It is not executed for each individual task that notifies it. This is key and one of the main benefits of using handlers.
For you, this means SQL Server only restarts when the change requires it.
Examples
A few examples of when to use handlers is when making changes that require SQL Server to be restarted.
- Instant File Initialization (IFI)
- Controlled by the Windows privilege, Perform Volume Maintenance Tasks.
- Needs to be granted to the SQL Server Engine service account.
- SQL Server won't use IFI until it's restarted.
- Lock Pages in Memory
- Controlled by the Windows privilege, Lock pages in memory.
- Prevents SQL Server memory from being paged out under OS pressure.
- Changes don't apply until SQL Server is restarted.
- Generate Security Audits
- Controlled by the Windows privilege, Generate security audits.
- Required when SQL Server needs to write entries to the Windows security log.
- Takes effect only after the SQL Server Engine service restarts.
Playbook
Let's look at the playbook below.
---
- name: Configure SQL Server Service Account Rights
hosts: sqlservers
gather_facts: true
vars:
sql_service_account: "SANDBOX\\svc_PROD_SqlEng$"
sql_svc: "MSSQLSERVER"
sql_action: "add"
handlers:
- name: Restart SQL Server
ansible.windows.win_service:
name: "{{ sql_svc }}"
state: restarted
force_dependent_services: true
tasks:
- name: Enable Instant File Initialization for SQL Server service account
ansible.windows.win_user_right:
name: SeManageVolumePrivilege
users: "{{ sql_service_account }}"
action: "{{ sql_action }}"
notify: Restart SQL Server
- name: Grant Lock Pages in Memory right to SQL Server service account
ansible.windows.win_user_right:
name: SeLockMemoryPrivilege
users: "{{ sql_service_account }}"
action: "{{ sql_action }}"
notify: Restart SQL Server
- name: Grant Generate Security Audits right to SQL Server service account
ansible.windows.win_user_right:
name: SeAuditPrivilege
users: "{{ sql_service_account }}"
action: "{{ sql_action }}"
notify: Restart SQL Server
How it works:
- If any of these rights are already present, nothing changes, and the service is not restarted.
- If new rights are added, Ansible notifies the handler to restart SQL Server once.
I'll execute this playbook while specifying "add" as the action to take.
ansible-playbook playbook_handlers.yml --limit PRDSQL1.SANDBOX.LOCAL -e "sql_action=add"This results in adding the 3 permissions and notifying the handler to execute.
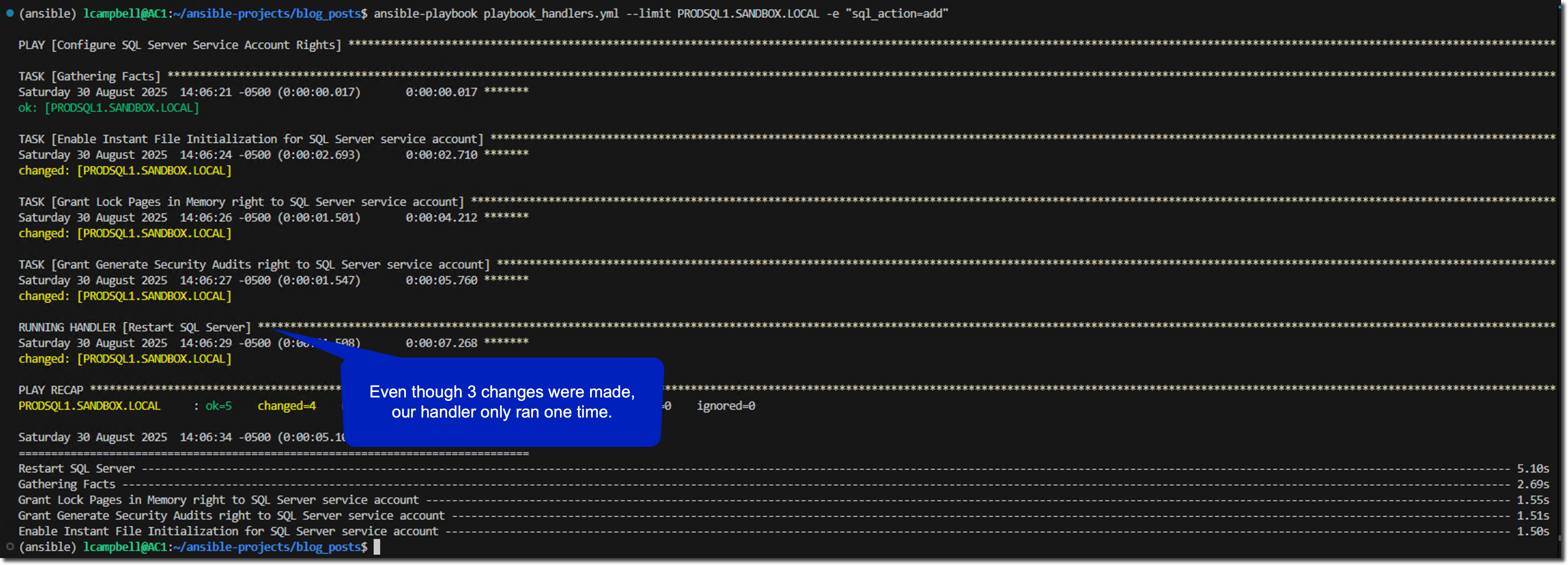
Running the playbook again, specifying the same action, results in no changes, and the handler is not notified.
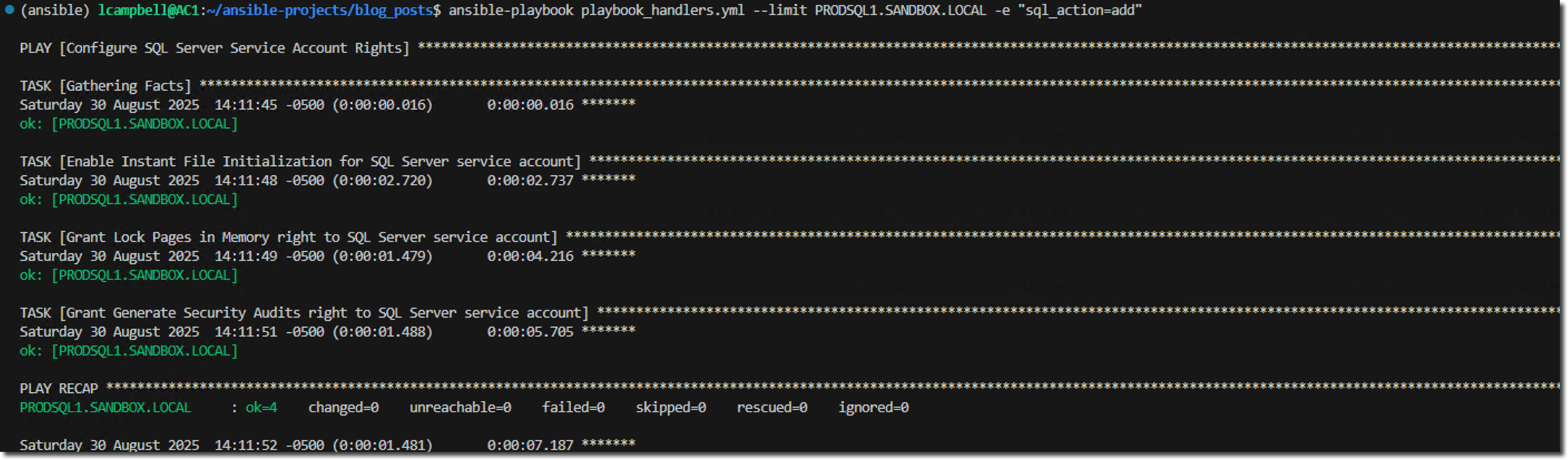
Why This Matters
Restarting the service only once, and only when a change is made, avoids needless downtime. The playbook is idempotent since we're using the win_user_right module from the Windows collection.
The playbook can be scaled to apply these permissions to multiple SQL Server instances in parallel with ease.
Conclusion
Handlers are a small concept with a big impact. They represent the difference between:
- Fragile scripts that force downtime, and automation frameworks that act intelligently.
Next time you're configuring privileges like IFI, Lock Pages in Memory, or Generate Security Audits, let a handler decide if SQL Server really needs a restart. That's automation with intelligence, and downtime avoided.
Get free access to my "SQL Server Automation: Your First Steps with Ansible" Guide
Get started with Ansible using this free guide. You'll discover how simple Ansible is to use, understand core concepts, and create two simple playbook examples.
When you signup, we'll send you periodic emails with additional free content.
